Modern Back and Neck Clinic Newsletter |
December 2019 www.modernbackandneckclinic.com |
|
Hyaluronic Acid 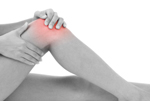 Hyaluronic acid is a substance found naturally in the body. The highest amounts are found in the eyes and joints. Hyaluronic acid helps to cushion and lubricate the joints. You can determine the extent of joint damage by measuring the length of hyaluronan in synovial fluid. Hyaluronic acid is taken orally, topically applied, or injected. Uses for hyaluronic acid Hyaluronic acid is injected into the eye during cataract removal, corneal transplantation, repair of detached retinas, and other eye problems. Hyaluronic acid is used as a lip filler in cosmetic surgery. Restylane is a popular wrinkle filler that is made from hyaluronic acid. Some people use topical hyaluronic acid as a moisturizer or for wound treatment. However, enough evidence does not exist to recommend its usage for wounds or burns. It also is commonly used and effective for healing mouth sores. Note: No proof exists to indicate that taking hyaluronic acid by mouth or applying it to skin helps to minimize the signs of aging. Side effects of hyaluronic acid When injected into the eye, some people report increased pressure in the eye. Hyaluronic acid rarely causes allergic reactions. It is not recommended during pregnancy or while breastfeeding at this time. References and recommended readings MedicineNet, Inc. Hyaluronic acid. Available at: http://www.medicinenet.com/hyaluronic_acid/article.htm. Accessed May 26, 2010. Wang CT, Lin J, Chang CJ, Lin YT, Hou SM. Therapeutic effects of hyaluronic acid on osteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am [serial online]. 2004;86:538-545. Available at: http://www.udel.edu/PT/clinic/journalclub/old/sojournalclub/03_04/april04/jbjs%20knee%20hylauronic%20acid.pdf. Accessed May 26, 2010. WebMD. Hyaluronic acid. Available at: |
|
|
|
